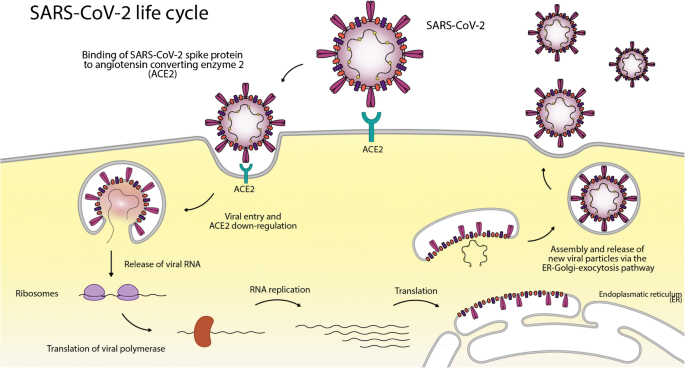
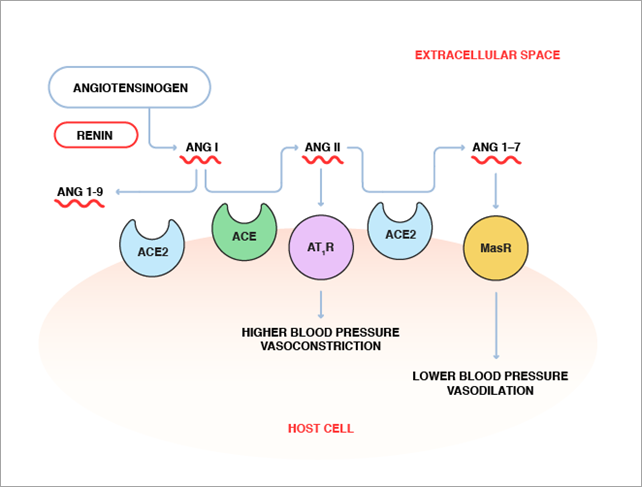
Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2: SARS-CoV-2 Receptor and Regulator of the Renin-Angiotensin System | Circulation Research

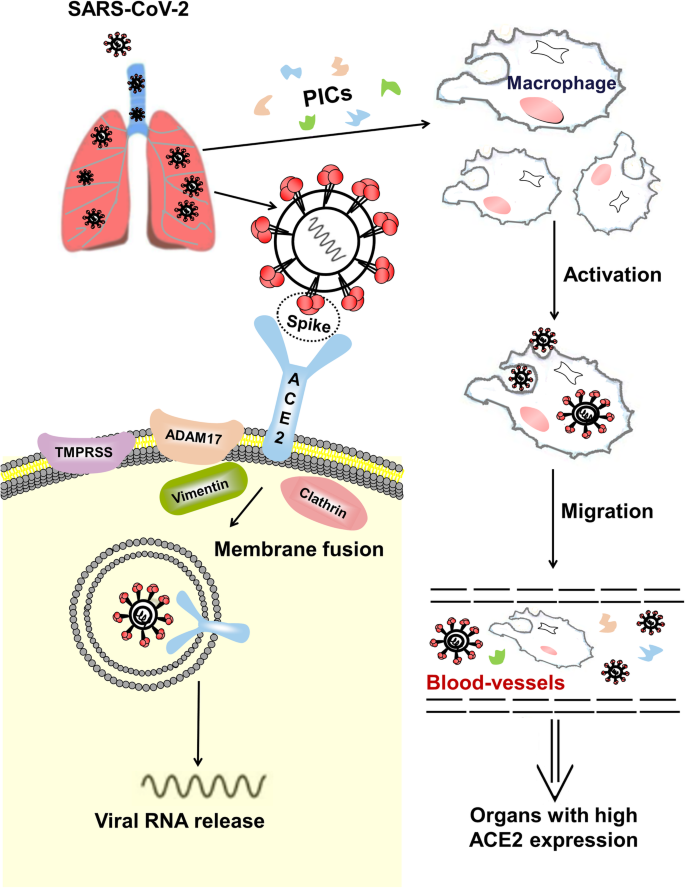
Protective role of ACE2 and its downregulation in SARS-CoV-2 infection leading to Macrophage Activation Syndrome: Therapeutic implications - ScienceDirect

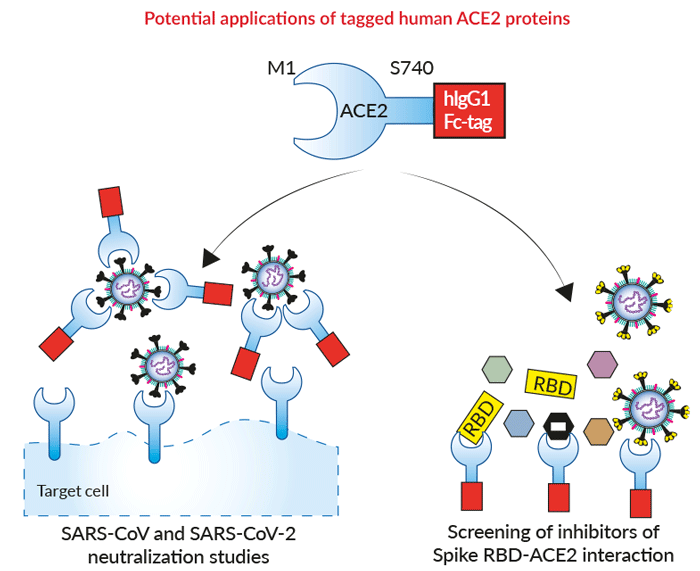
Molecular interaction and inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 binding to the ACE2 receptor | Nature Communications

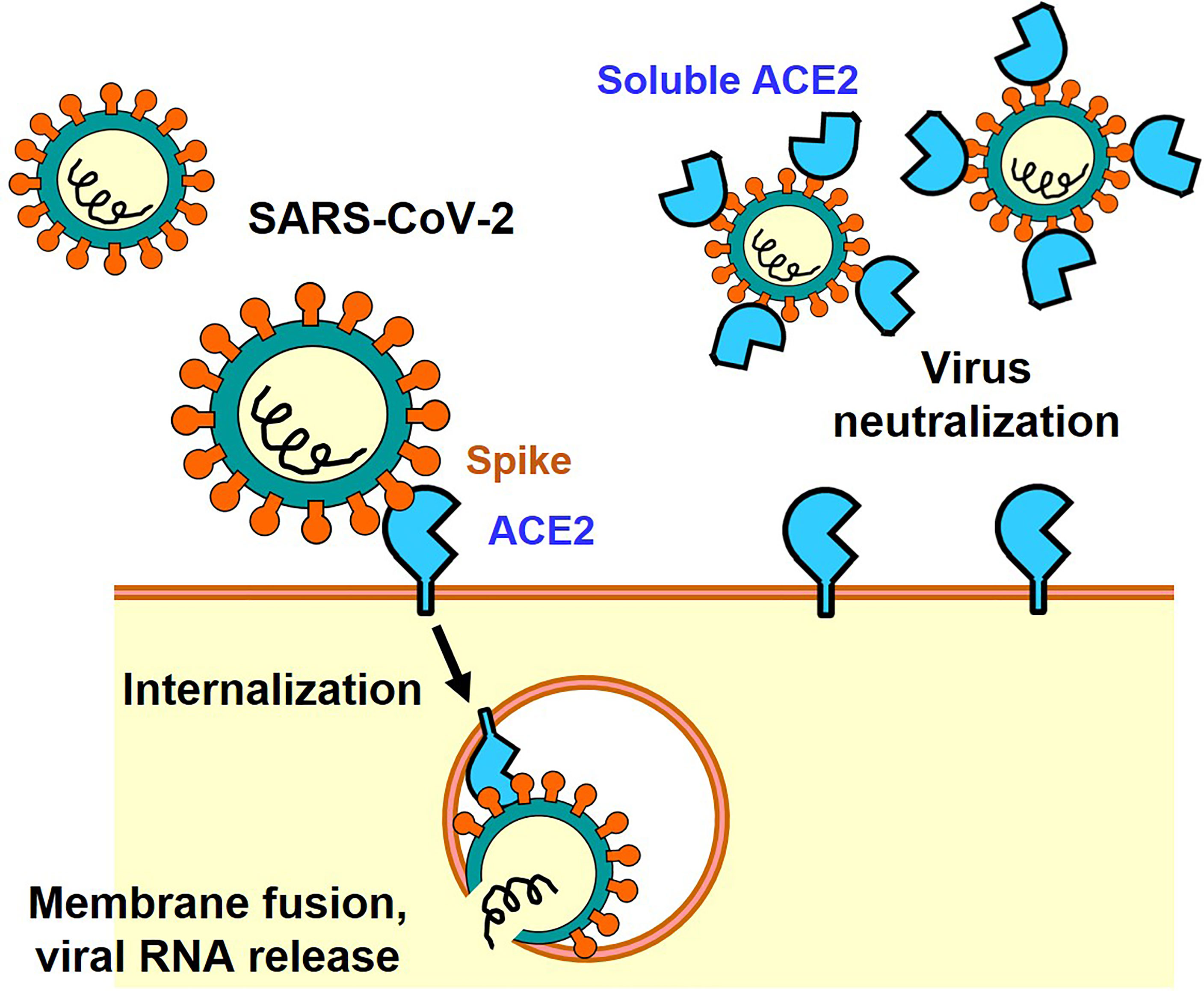
Soluble ACE2-mediated cell entry of SARS-CoV-2 via interaction with proteins related to the renin-angiotensin system - ScienceDirect

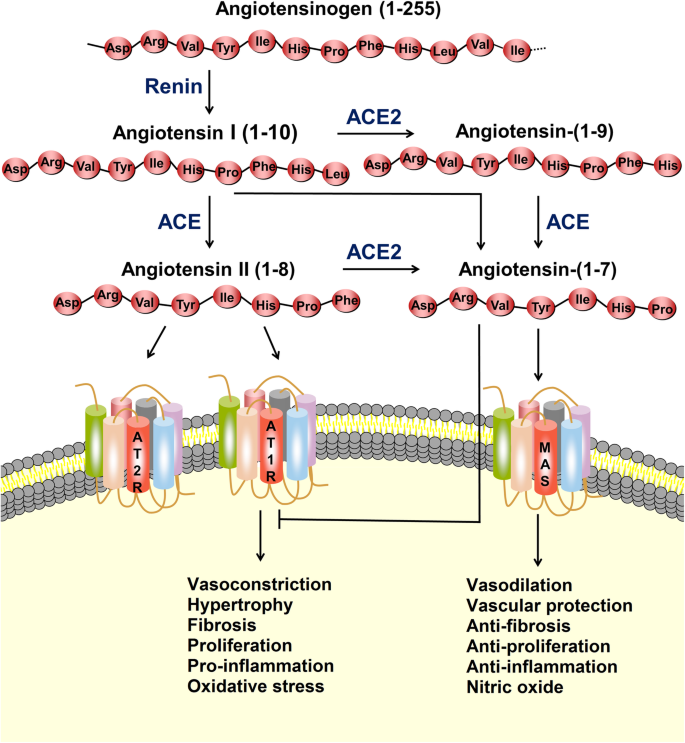
SARS-CoV-2 receptor ACE2-dependent implications on the cardiovascular system: From basic science to clinical implications - ScienceDirect
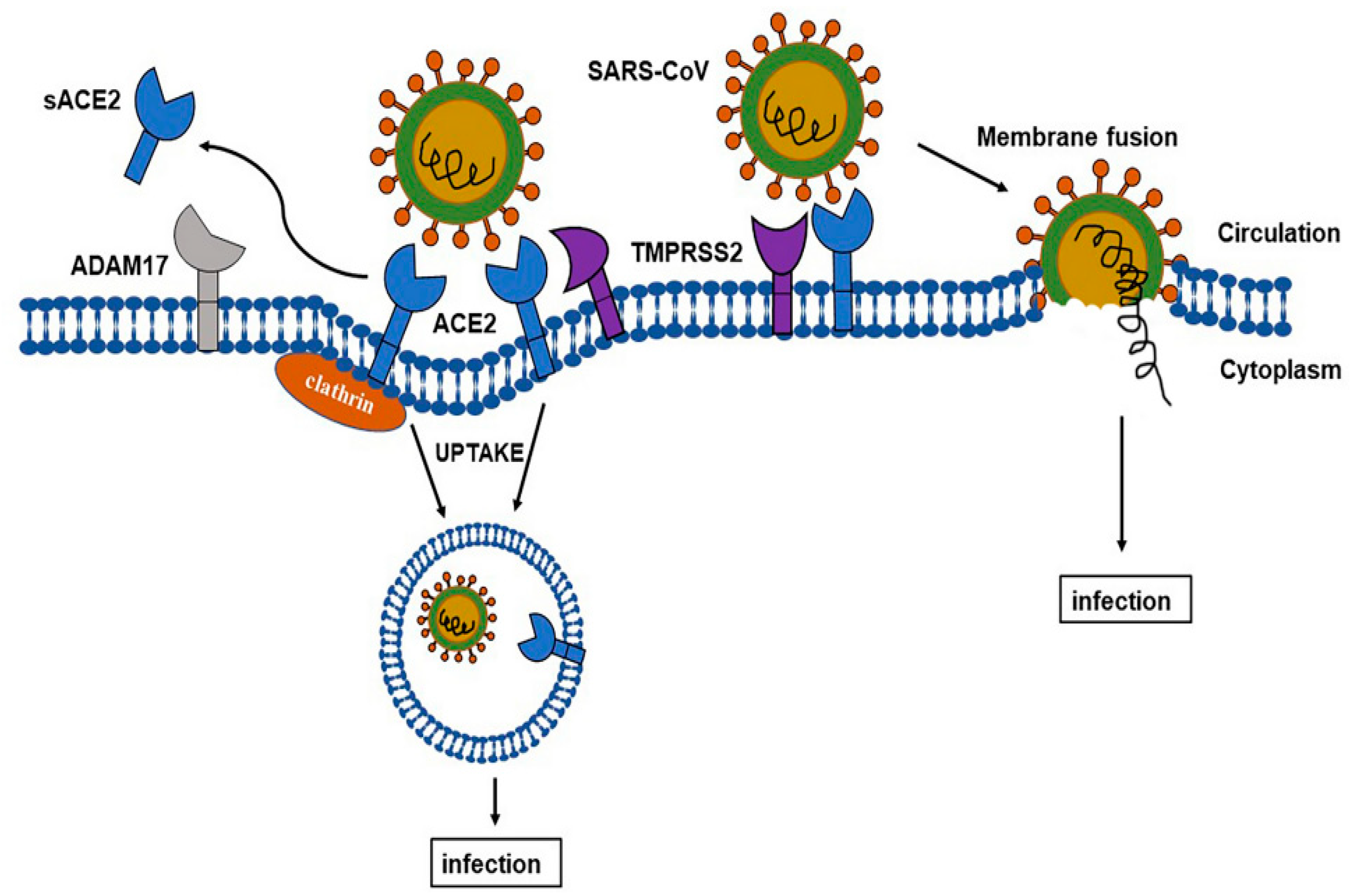
IJMS | Free Full-Text | Do Changes in ACE-2 Expression Affect SARS-CoV-2 Virulence and Related Complications: A Closer Look into Membrane-Bound and Soluble Forms

Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID‐19) and Cardiovascular Disease: A Viewpoint on the Potential Influence of Angiotensin‐Converting Enzyme Inhibitors/Angiotensin Receptor Blockers on Onset and Severity of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 ...

Debulking SARS-CoV-2 in saliva using angiotensin converting enzyme 2 in chewing gum to decrease oral virus transmission and infection: Molecular Therapy

Transcriptional regulation and small compound targeting of ACE2 in lung epithelial cells | Acta Pharmacologica Sinica
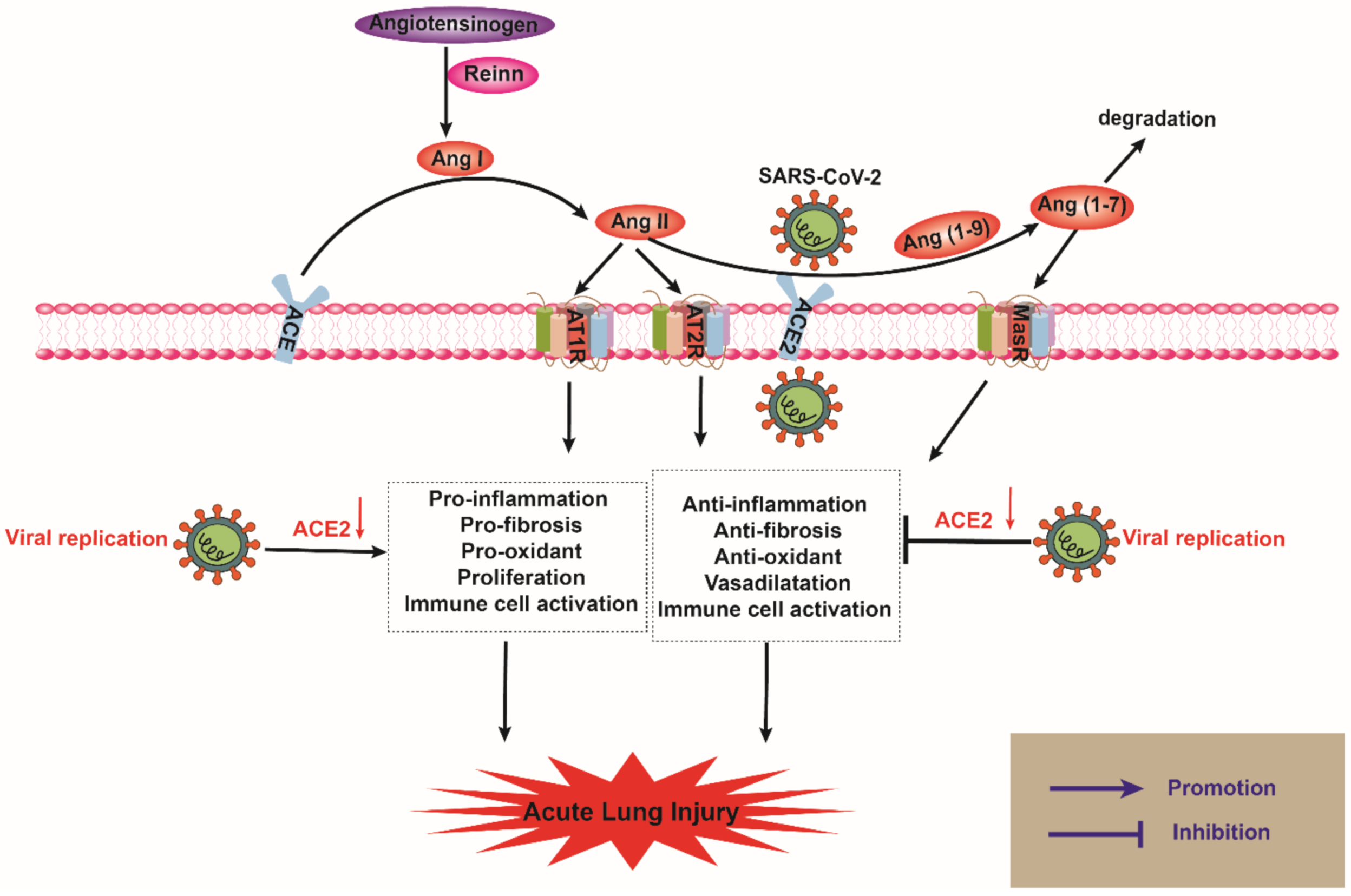
IJMS | Free Full-Text | ACE2 and Innate Immunity in the Regulation of SARS-CoV-2-Induced Acute Lung Injury: A Review

SARS-CoV-2 and ACE2: The biology and clinical data settling the ARB and ACEI controversy - eBioMedicine
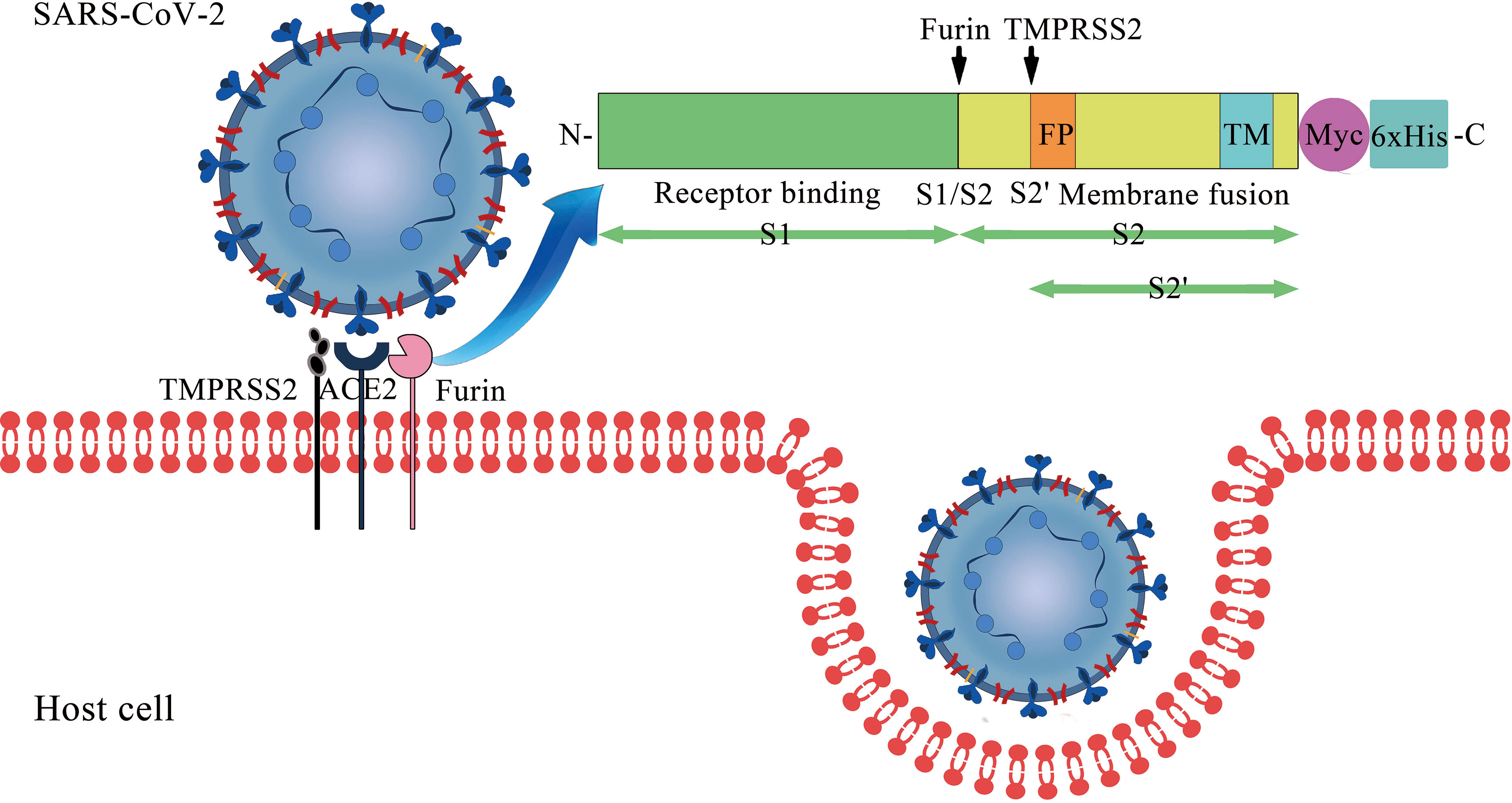
Frontiers | The Impact of ACE2 Polymorphisms on COVID-19 Disease: Susceptibility, Severity, and Therapy

COVID-19 and ACE -inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers-: The need to differentiate between early infection and acute lung injury | Revista Colombiana de Cardiología